Androgenetic alopecia, also called common baldness in men and hereditary loss in women, is the most common cause of hair loss in men and women. A common trait, from the genetic point of view, is that it is produced by androgens in men and sensitivity to them in women.
It can begin during adolescence or early adulthood in both sexes and manifest itself fully at the age of 40.
According to various statistics, it affects about 25% of men between 25 and 35, 40% in their 40s, and 50% over 50, with a rising percentage in groups we consider to be the elderly. In women it can affect as much as about 28%, although there are no detailed studies on the subject.
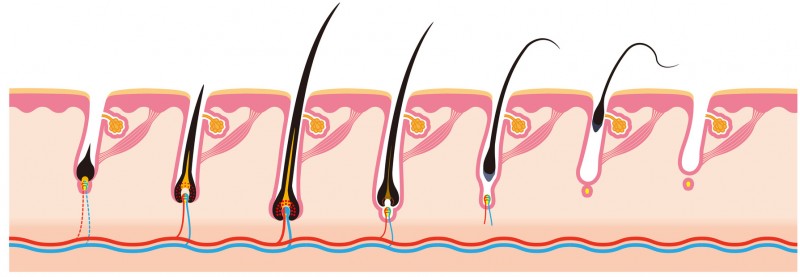
For proper understanding of alopecia, we must start by saying that hair growth is cyclical and goes through three phases:
1º growth phase (anagen), which lasts from 2 to 6 years, where the hair grows 1cm every month.
2º transistional phase (catagen), lasting about 3 weeks
3º resting phase (telogen), between 80-100 hairs imperceptibly fall a day for about 3 or 4 months.






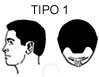
 Hair Loss with small recessions in the fronto-temporal scalp area.
Hair Loss with small recessions in the fronto-temporal scalp area.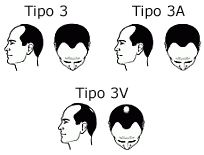
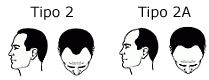
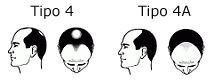 In this type, loss of hair is more extended than type III, with little or no hair on top of the head.
In this type, loss of hair is more extended than type III, with little or no hair on top of the head.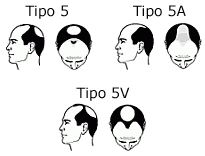 In this phase, the bald patch is still separated from the fronto-temporal region, although this separation is not so obvious because the strip of hair that crosses the upper part of the scalp has increasingly thinned and the hair has become sparse.
In this phase, the bald patch is still separated from the fronto-temporal region, although this separation is not so obvious because the strip of hair that crosses the upper part of the scalp has increasingly thinned and the hair has become sparse.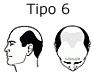 This case occurs when the balding patch couples with fronto-temporal balding, and becomes one.
This case occurs when the balding patch couples with fronto-temporal balding, and becomes one.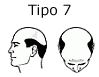 This is the most severe form of hair loss, there is only a fringe of hair like a horseshoe, which begins in front of the ear and extends toward the rear of the scalp and neck.
This is the most severe form of hair loss, there is only a fringe of hair like a horseshoe, which begins in front of the ear and extends toward the rear of the scalp and neck.


